How Integration with Existing Systems Drives Business Success
Achieve seamless business operations with effective integration with existing systems. Explore strategies, best practices, and modern technologies in 2025.

Companies use a variety of software programs to effectively manage operations in the fast-paced corporate world of today. From customer relationship management (CRM) tools and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to cloud-based analytics and AI-driven platforms, businesses utilize a complex ecosystem of applications. According to a 2025 survey, over 78% of enterprises reported challenges in integrating new technologies with their existing systems, highlighting the critical importance of seamless integration. Achieving effective integration with existing systems is not just a technical necessity—it is a strategic imperative that can determine an organization’s ability to innovate, scale, and remain competitive.
The ability to integrate new tools and technologies with legacy systems ensures smooth data flow, enhances operational efficiency, and minimizes disruptions. For businesses exploring AI, cloud computing, or advanced analytics, integration is often the first step toward digital transformation. Companies that master integration are better equipped to harness the full potential of technology, turning fragmented systems into cohesive, intelligent workflows.
What is Integration with Existing Systems?
Integration with existing systems refers to the process of connecting new software, applications, or technologies with the current IT infrastructure to enable seamless communication, data exchange, and operational harmony. Rather than replacing existing systems entirely—which can be costly, time-consuming, and risky—integration allows organizations to leverage their existing investments while adopting new solutions.
Key goals of system integration include:
-
Data Consistency: Ensuring that all platforms access the same up-to-date information.
-
Operational Efficiency: Reducing manual data entry and eliminating redundant processes.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Providing unified, real-time insights across systems.
-
Scalability: Allowing the business to grow without overhauling the IT infrastructure.
In essence, integration is the backbone of a connected, data-driven organization.
Why Integration with Existing Systems is Crucial
1. Streamlined Workflows
When different systems are disconnected, employees must manually transfer data, which is time-consuming and error-prone. Integration automates these processes, allowing seamless workflows that improve productivity and reduce operational bottlenecks.
2. Cost Savings
Replacing entire systems is expensive. By integrating new solutions with existing platforms, businesses can extend the life of their current systems, reduce licensing costs, and minimize downtime during implementation.
3. Data Accuracy and Reliability
Manual processes often lead to discrepancies and errors. Integration ensures that data is consistent across all systems, enabling more accurate reporting, analysis, and decision-making.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience
Integration allows customer-facing systems, like CRM platforms, to synchronize with marketing automation tools, support systems, and analytics platforms. This ensures that customers receive personalized, timely, and accurate interactions, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Facilitating Innovation
Seamless integration opens doors for adopting advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT. These technologies rely on data from multiple sources to generate insights, making integration a prerequisite for innovation.
Types of System Integration
1. Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration connects multiple systems across departments or functions. For example, integrating HR software with payroll systems and attendance management tools ensures consistent employee data across all platforms.
2. Vertical Integration
Vertical integration connects systems across different hierarchical levels within an organization. For instance, integrating ERP software with operational management systems allows executives to monitor production metrics in real time.
3. Star Integration
Also called point-to-point integration, star integration connects each system directly to every other system. While effective for smaller organizations, it becomes complex and difficult to manage as the number of systems grows.
4. Middleware Integration
Middleware acts as an intermediary layer that facilitates communication between disparate systems. It simplifies integration by standardizing data exchange, reducing the need for multiple point-to-point connections.
5. API-Based Integration
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become the standard for modern integration. They allow different systems to communicate through standardized protocols, enabling real-time data exchange and extending the functionality of existing systems.
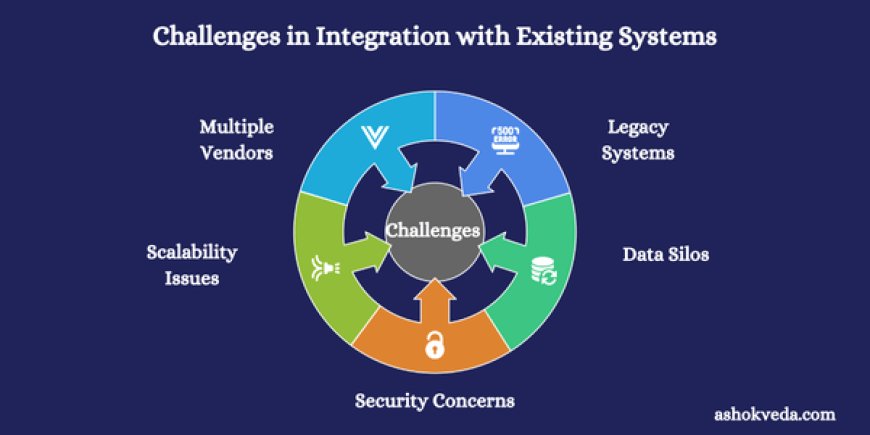
Challenges in Integration with Existing Systems
Despite its benefits, integration can be complex and comes with several challenges:
1. Legacy Systems
Older systems may lack modern interfaces or APIs, making integration difficult. Custom connectors or middleware are often required to bridge these gaps.
2. Data Silos
Data stored in isolated systems can be inconsistent, outdated, or incomplete, making integration more challenging. Consolidating and cleaning data is often necessary before integration.
3. Security Concerns
Integrating multiple systems increases the number of access points, potentially exposing sensitive data. Ensuring secure data exchange and compliance with regulations is critical.
4. Scalability Issues
Integration solutions must be designed to handle future growth. Poorly planned integration can create bottlenecks as data volume and user demand increase.
5. Complexity of Multiple Vendors
Organizations often use software from multiple vendors. Ensuring seamless communication between these platforms requires careful planning, testing, and monitoring.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
To maximize the benefits of integration, organizations should adopt a strategic approach:
1. Conduct a System Audit
Assess all existing systems, workflows, and data sources to understand integration requirements. Identify redundant systems and determine which platforms are essential for your operations.
2. Define Clear Objectives
Establish what you want to achieve with integration—whether it’s reducing manual processes, enhancing customer experience, or enabling advanced analytics.
3. Choose the Right Integration Approach
Decide whether API-based, middleware, or hybrid integration is suitable based on system compatibility, scalability, and budget.
4. Ensure Data Consistency
Standardize data formats, clean existing data, and define rules for data synchronization to maintain accuracy across systems.
5. Prioritize Security
Implement encryption, access controls, and compliance measures to protect sensitive data during integration.
6. Test Thoroughly
Before going live, perform extensive testing to ensure that systems communicate effectively, data is accurate, and workflows are uninterrupted.
7. Monitor and Optimize
Integration is not a one-time task. Continuously monitor system performance, resolve issues promptly, and optimize workflows as business needs evolve.
Technologies Enabling Seamless Integration
Several technologies and platforms facilitate smooth integration with existing systems, including
-
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB): Connects applications within an enterprise using a centralized architecture.
-
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service): Cloud-based solutions that simplify integration across on-premises and cloud systems.
-
API Management Tools: Platforms like Apigee, Postman, and MuleSoft manage APIs for secure, scalable communication.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automates repetitive tasks and facilitates data transfer between systems.
-
Data Warehousing and ETL Tools: Tools like Talend, Informatica, and Snowflake help consolidate and transform data for seamless integration.
Benefits of Integration with Existing Systems
Successful integration can drive measurable business outcomes:
-
Improved Efficiency: Automated workflows save time and reduce errors.
-
Cost Reduction: Maximizes ROI from existing systems and minimizes operational expenses.
-
Better Insights: Unified data provides actionable insights for strategic decisions.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: Consistent information across touchpoints strengthens customer satisfaction.
-
Agility and Scalability: Businesses can quickly adopt new technologies without disrupting operations.
In the era of digital transformation, integration with existing systems is no longer optional—it is essential. Organizations that master system integration gain a competitive edge, improve operational efficiency, and unlock the potential of advanced technologies like AI, analytics, and IoT. By addressing challenges proactively, adopting best practices, and leveraging modern integration technologies, businesses can create cohesive, intelligent systems that support growth and innovation. Investing in integration today ensures that organizations remain agile, data-driven, and ready to embrace the technologies of tomorrow. The future of business operations hinges on the ability to connect, automate, and optimize systems, making integration a strategic priority for all forward-thinking enterprises.