Data Security in the Contemporary World
Learn how to keep your information safe online. Discover ways to protect your data in today's digital world
In the Contemporary World, keeping our information safe is a big worry for everyone, whether you're a person or a big company. Lots of important stuff, like our personal details or work files, are all stored and sent through computers. But, there's a problem. Hackers try to sneak in and steal this info, causing a mess. This makes folks really nervous about their privacy and security. It's like a tricky puzzle: how do we make sure our data stays safe while we keep using all this amazing technology? Figuring this out is super important to protect what matters most to us.
Data security has a lot of problems. Hackers always find new ways to break into systems and steal things. Even the best security can't always stop them. Also, many people don't realize how important it is to keep data safe. They do things that aren't safe, making the problem worse. When people don't know how to be safe with data, it makes it easier for hackers to take important information. This lack of awareness and risky behavior makes data security a big challenge that needs more attention to protect sensitive information.
How can individuals, organizations, and governments move through this intricate perspective of data security threats? What strategies and technologies are available to mitigate these risks and ensure robust data protection in the contemporary world?
Data Security Measures
Encryption: This security technique scrambles data into an unreadable format using complex algorithms. Even if a hacker intercepts the data, without the decryption key, it's practically impossible to make sense of the information. It's like converting a secret message into a code that only the intended recipient can decipher.
Firewalls: Think of a firewall as a digital gatekeeper. It monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It blocks potentially harmful data while allowing legitimate information to pass through. It's akin to having a bouncer at a club, checking IDs to permit entry to the right people.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): This method adds an extra layer of protection beyond passwords. It requires users to verify their identity using two or more independent credentials. For instance, logging in with a password and then confirming identity via a code sent to a mobile device. It's like having both a key and a security code to access a vault.
Regular System Updates: Software updates aren't just about adding new features; they also patch security vulnerabilities. Hackers often exploit weaknesses in outdated software. Regular updates ensure that known security holes are fixed, reducing the chances of a breach. It's like regularly maintaining your home to prevent break-ins by fixing weak spots.
Human Element: Training and Awareness
Recognizing Phishing: Training individuals to identify signs of phishing emails or messages. This includes spotting suspicious links, requests for personal information, or urgent messages that create a sense of panic. Educating users to scrutinize before clicking reduces the chances of falling prey to cybercriminals.
Strong Password Practices: Encouraging the use of complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Emphasizing the importance of not sharing passwords and using different ones for different accounts helps fortify digital security. Password managers can also assist in creating and storing strong passwords securely.
Emerging Technologies: AI and Blockchain
AI-powered Cybersecurity Systems: AI analyzes patterns and behaviors in vast amounts of data to identify anomalies that might indicate a threat. It enables systems to learn from previous attacks and adapt defenses in real time, acting as an intelligent shield against evolving threats.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain stores data in blocks that are chained together and secured using cryptographic principles. Each block contains a record of transactions that cannot be altered retroactively. It creates a tamper-resistant digital ledger, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of data manipulation.
Compliance and Regulations
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): GDPR mandates strict guidelines on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored. It gives individuals control over their data and imposes hefty fines for non-compliance. Complying with GDPR involves obtaining explicit consent for data collection, ensuring data portability, and maintaining stringent security measures.
Challenges in AI Security
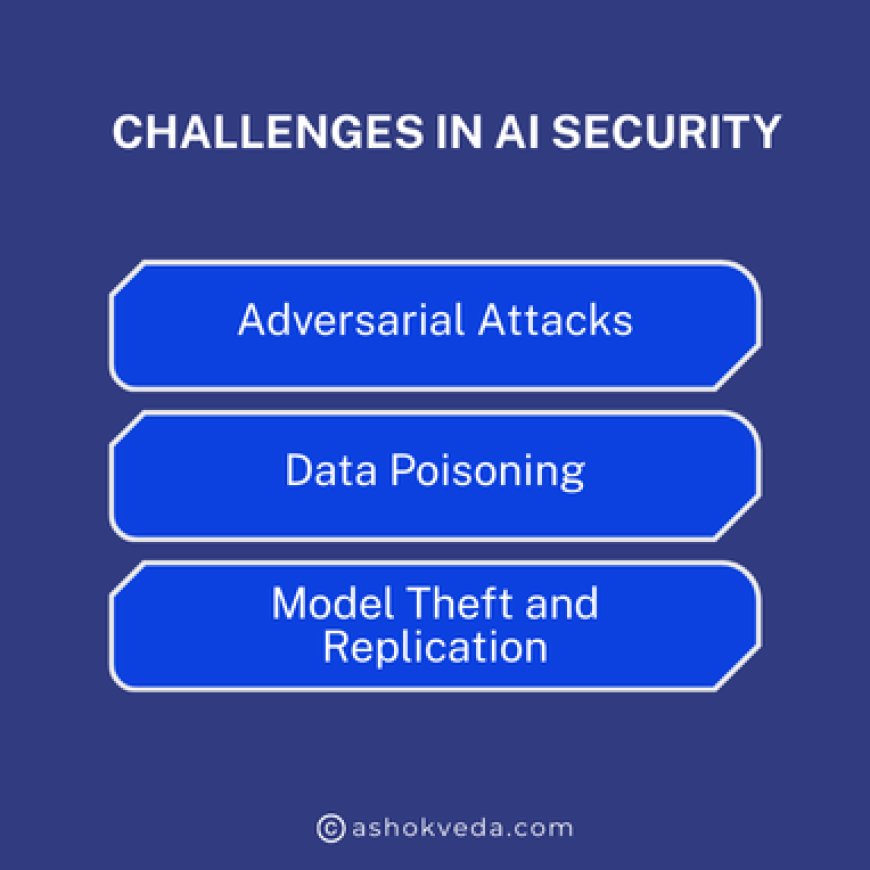
Adversarial Attacks: These attacks aim to trick AI systems by making small changes in data, fooling them into making mistakes. For instance, slight alterations in images might confuse AI-based image recognition, causing it to identify things incorrectly. Hackers use these subtle changes to manipulate AI systems, causing potential chaos in their operations.
Data Poisoning: Bad actors intentionally insert false or misleading data into AI training sets. This tampering corrupts the learning process, causing AI models to develop biases or inaccuracies. It's like mixing bad ingredients into a recipe, resulting in flawed or skewed AI models that make wrong decisions.
Model Theft and Replication: Theft of trained AI models is a worry, particularly when these models contain proprietary or sensitive information. Unauthorized access to these models can lead to misuse or manipulation. Additionally, replicating stolen models can result in unauthorized usage, posing a threat to intellectual property and the integrity of AI-driven systems.
Strategies for AI Security
Robust Data Integrity: Ensuring the integrity and quality of training data is crucial. Verification mechanisms and data validation techniques help detect and mitigate instances of data poisoning or corruption.
Adversarial Defense Techniques: Employing techniques such as adversarial training, where AI models are trained on adversarially generated examples, helps make AI systems more robust against adversarial attacks.
Secure Model Deployment: Implementing secure protocols for deploying AI models, including encryption of model parameters and using secure channels for communication, prevents unauthorized access or tampering.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Regular monitoring of AI systems helps identify anomalies or potential threats. Implementing updates and patches to address vulnerabilities is essential to keep AI systems secure.
Ethical and Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to ethical guidelines and regulatory standards ensures that AI systems are developed and used in an ethical and lawful manner, protecting against potential misuse or breaches of trust.
It is crucial that we take data security seriously and implement effective measures to protect our information. This includes using strong passwords, regularly updating software and security systems, and being vigilant about suspicious activity. It is also important for organizations to invest in robust security protocols and provide training and education to employees. By taking these steps, we can help ensure that our data remains safe and secure in the contemporary world.